Climate change has far-reaching effects on various ecosystems and species across the globe. One group of animals that is impacted by climate change is birds, including pigeons. As temperatures and weather patterns shift, pigeons and other bird species must adapt to new conditions, altering their behavior, migration patterns, and even their physical characteristics. This article will explore the connections between pigeons and climate change, highlighting the ways in which these birds are affected by the changing climate.
Key Takeaways
- Climate change impacts birds in various ways, including changes in their behavior, range, migration patterns, and physical characteristics.
- Warming temperatures are influencing where birds live and breed, causing shifts in their distribution.
- Birds rely on specific environmental cues and timing for migration, breeding, and feeding, which can be disrupted by climate change.
- Indirect effects of climate change, such as habitat loss and ecosystem disruptions, also impact bird populations, including pigeons.
- Conservation efforts and reducing carbon emissions can help mitigate the impact of climate change on birds and their habitats.
Shifting Ranges and Distribution of Pigeons
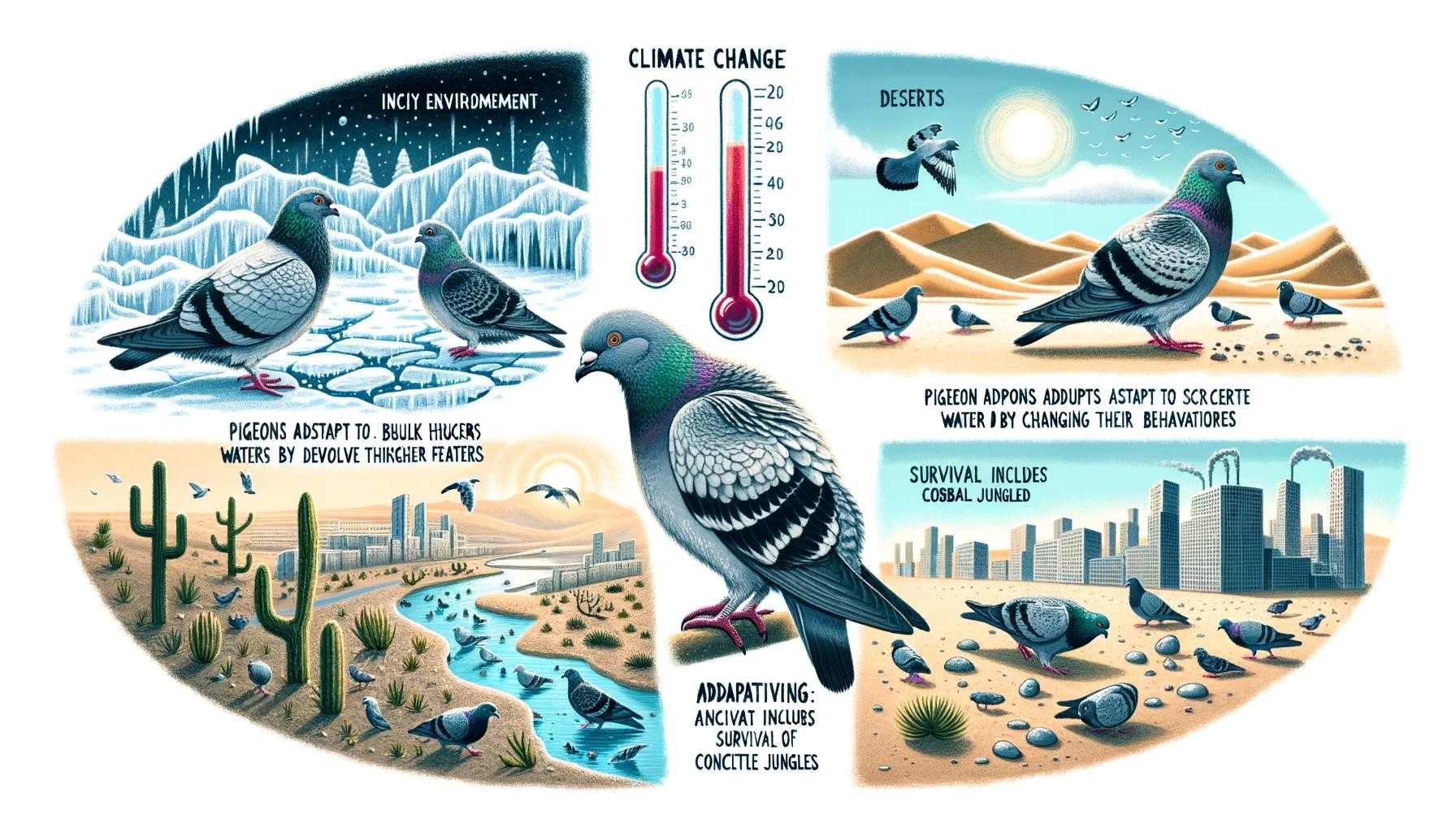
One of the notable impacts of climate change on pigeons and other bird species is the shifting of their ranges and distribution. As temperatures rise, pigeons may be forced to move to higher latitudes or elevations to find suitable habitats.
Long-term studies have shown that many bird species, including pigeons, are shifting their winter and breeding ranges northward. For example, Christmas Bird Count data spanning several decades indicate that many bird groups, such as woodpeckers and large forest birds, are more likely to be observed farther north now than in previous decades.
Migratory bird species are also changing their timing. Birds are arriving in North America during springtime approximately two days earlier per decade since the 1990s. These shifts in timing and range are driven by climate change as birds respond to changes in temperature and vegetation patterns.
Altered Behavior and Migration Patterns
Climate change can disrupt the natural cues that birds, including pigeons, rely on for migration, breeding, and feeding. Changes in temperature and weather patterns can affect the availability of food and nesting sites, as well as the timing of key events in a bird’s life cycle.
For example, birds may need to adjust the timing of their migration to match changes in the timing of food availability or favorable weather conditions. If migratory birds don’t adjust their timing accordingly, they may experience a mismatch between their arrival and the availability of critical resources, potentially impacting their survival and reproductive success.
Pigeons, like many other bird species, have evolved to time their migrations based on environmental cues, such as day length and temperature. However, these cues may change due to climate change, disrupting the precise timing and synchronization of migration patterns.
Physical Characteristics and Adaptation
Climate change can also influence the physical characteristics of pigeons and other bird species. Researchers have observed that as global temperatures increase, birds’ bodies are getting smaller, while their wings are getting longer.
This change in body size may help birds disperse excess body heat in warming habitats. Smaller bodies have a larger surface area relative to their volume, allowing for greater heat dissipation. Additionally, longer wings may help birds cope with increased wind and turbulent air currents associated with changing weather patterns.
However, it’s important to note that not all bird species exhibit these physical changes in response to climate change. The effects of climate change on physical characteristics can vary among species, depending on their ecological niche and specific adaptations to their environment.
Conservation and Mitigation Efforts
Given the impact of climate change on birds, including pigeons, it is crucial to implement conservation measures and reduce carbon emissions to mitigate further harm.
Efforts to protect and restore bird habitats are essential, including preserving natural areas, creating bird-friendly landscapes, and reducing threats such as habitat loss, outdoor cat predation, and collisions with buildings.
Individuals can also contribute by reducing their carbon footprint through sustainable practices, such as energy conservation, using renewable energy sources, and supporting policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, education and awareness about the impacts of climate change on birds and the importance of conservation can help inspire collective action to protect these vital species.
In conclusion, climate change profoundly affects pigeons and other bird species. The warming temperatures, altered behavior, changing migration patterns, and physical adaptations all highlight the interconnectedness between birds and their environment. By understanding these impacts and taking steps to mitigate climate change, we can help protect and conserve bird populations for future generations.