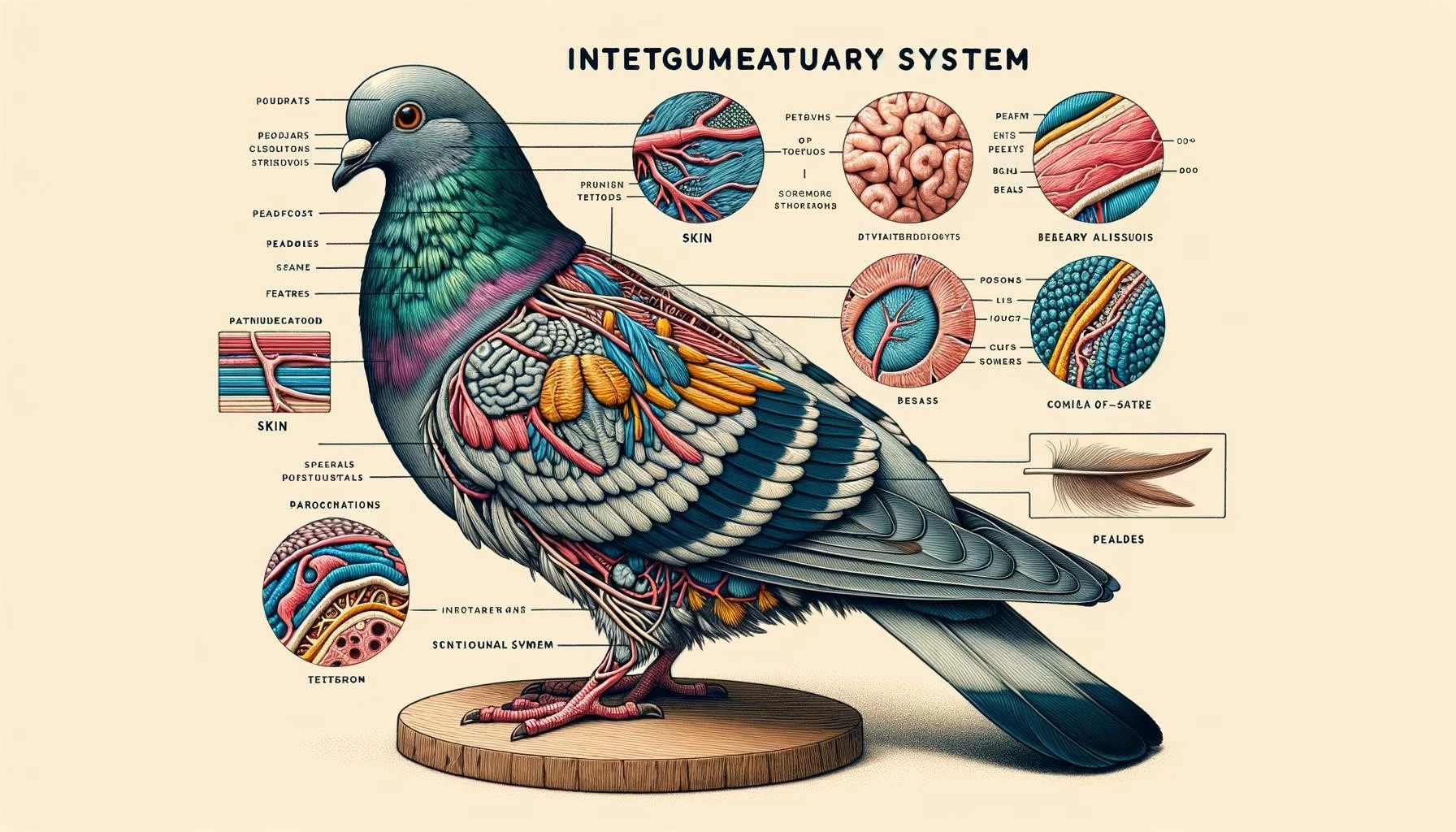
The integumentary system of a pigeon plays a crucial role in its overall physiology and survival. This system consists of the skin, feathers, and appendages such as claws and beak. The integumentary system serves various functions, including protection, thermoregulation, and communication. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of pigeon integumentary system in detail.
Key Takeaways
- The pigeon integumentary system consists of the skin, feathers, and appendages.
- It plays a vital role in protecting the bird’s internal organs and maintaining homeostasis.
- Feathers are a unique feature of birds and serve several functions, including flight, insulation, and display.
- The skin of a pigeon lacks sweat glands but contains other specialized glands, such as the preen gland.
- Pigeons possess a complex network of subcutaneous vessels in the skin, particularly over the neck, which aids in thermoregulation.
Anatomy of the Integumentary System
The integumentary system of a pigeon consists of several components, including the skin, feathers, and appendages. Let’s explore each of these components in detail:
1. Skin
The skin of a pigeon covers the majority of its body and provides a physical barrier between the internal and external environment. Avian skin is thin, elastic, and loosely attached to the body, allowing birds the freedom of movement needed for flight. Unlike mammals, birds do not have sweat glands in their skin. However, they do have specialized glands, such as the preen gland and the glands in the outer ear canal, which serve specific functions.
2. Feathers
Feathers are one of the defining features of birds and play a crucial role in the pigeon’s integumentary system. Feathers serve various functions, including flight, insulation, camouflage, and display. They are composed of a protein called keratin and are highly specialized structures. Feathers are arranged in a specific pattern on the body, with different types of feathers serving different purposes. For example, contour feathers provide the bird with its shape and streamline its body for efficient flight, while down feathers provide insulation.
Pigeons possess a complex arrangement of feathers, allowing them to fly with precision and navigate various environments, including urban areas. Feathers undergo regular molting, where old or damaged feathers are replaced with new ones. Molting is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the plumage and ensuring optimal flight performance.
3. Appendages
The appendages of the pigeon integumentary system include the claws and beak. The claws, also known as talons, are used for grasping and perching. They are made of keratin and are sharp and curved, enabling the bird to hold onto branches and other surfaces securely. The beak, or bill, is a specialized structure used for feeding, communication, and grooming. Pigeon beaks vary in shape and size depending on their diet and specific adaptations of the species.
Functions of the Integumentary System in Pigeons
The integumentary system performs several crucial functions in pigeons, ensuring their survival and well-being. Here are some significant functions:
1. Protection
The integumentary system acts as a protective barrier, shielding the pigeon’s internal organs from injury and pathogens in the environment. The skin acts as a physical barrier, preventing the entry of harmful substances and microbes. Feathers provide protection against abrasions and minor injuries, while the beak and claws are essential for defense and predation.
2. Thermoregulation
The integumentary system plays a crucial role in thermoregulation, allowing pigeons to maintain a constant body temperature. Feathers act as excellent insulators, trapping warm air close to the body and keeping the bird warm in cold environments. The complex network of subcutaneous vessels in the pigeon’s skin, particularly over the neck, helps regulate body temperature. By dilating or constricting these blood vessels, pigeons can adjust heat exchange with their environment.
3. Communication
The integumentary system also plays a role in communication among pigeons. Feathers, particularly in males, are often used for display during courtship and mating rituals. The condition, coloration, and arrangement of feathers can convey important information about the bird’s health, fitness, and reproductive status.
Overall, the integumentary system of pigeons is a complex and multifunctional system that is essential for their survival and adaptation to their environment. It provides protection, aids in thermoregulation, and plays a role in communication. Understanding the intricacies of the integumentary system helps us appreciate the remarkable adaptations of these birds.