Breeding pigeons successfully requires a blend of art and science, from understanding the reproductive process to maintaining genetic diversity within populations. The choice of breeding techniques, the creation of a conducive environment, and the provision of adequate nutrition, all contribute to a thriving pigeon population. Let’s delve into the intricacies of pigeon breeding, where the beauty of nature meets meticulous human effort, to produce remarkable results.
Key Takeaways
- Pigeon breeding success is dependent on understanding the reproductive process and implementing good breeding practices.
- Breeding techniques such as line-breeding, cross-breeding, and inbreeding are commonly used in pigeon breeding.
- Genetic diversity and selective breeding play important roles in maintaining the health and vitality of pigeon populations.
- Pigeons can breed year-round, but peak reproduction occurs in the spring and fall.
- Creating a comfortable breeding environment, providing adequate nutrition, and caring for breeder birds are crucial for breeding success.
Pigeon breeding success is determined by various factors, including understanding the reproductive process and implementing good breeding practices. Successful pigeon breeders pay attention to the anatomy of pigeon breeding success, which includes:
- Understanding the reproductive process: Breeding pigeons involves knowing the optimal conditions for successful mating, egg laying, and incubation. Pigeons have short reproductive cycles, with an incubation period of just 17-19 days, allowing them to produce multiple clutches.
- Implementing good breeding practices: Breeding pigeons is both an art and a science. It requires attention to detail, dedication, and creating a comfortable breeding environment for the pigeons. The use of high-quality breeder cages, proper nutrition, and care of breeder birds are essential.
- Using breeding techniques: Pigeon breeders may employ different breeding techniques such as line-breeding, cross-breeding, and inbreeding to achieve their desired traits in offspring. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, and breeders must understand how to use them effectively.
- Maintaining genetic diversity: Genetic diversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and vitality of pigeon populations. Pigeon breeders must carefully select breeding pairs to maintain diverse gene pools and avoid detrimental effects of inbreeding.
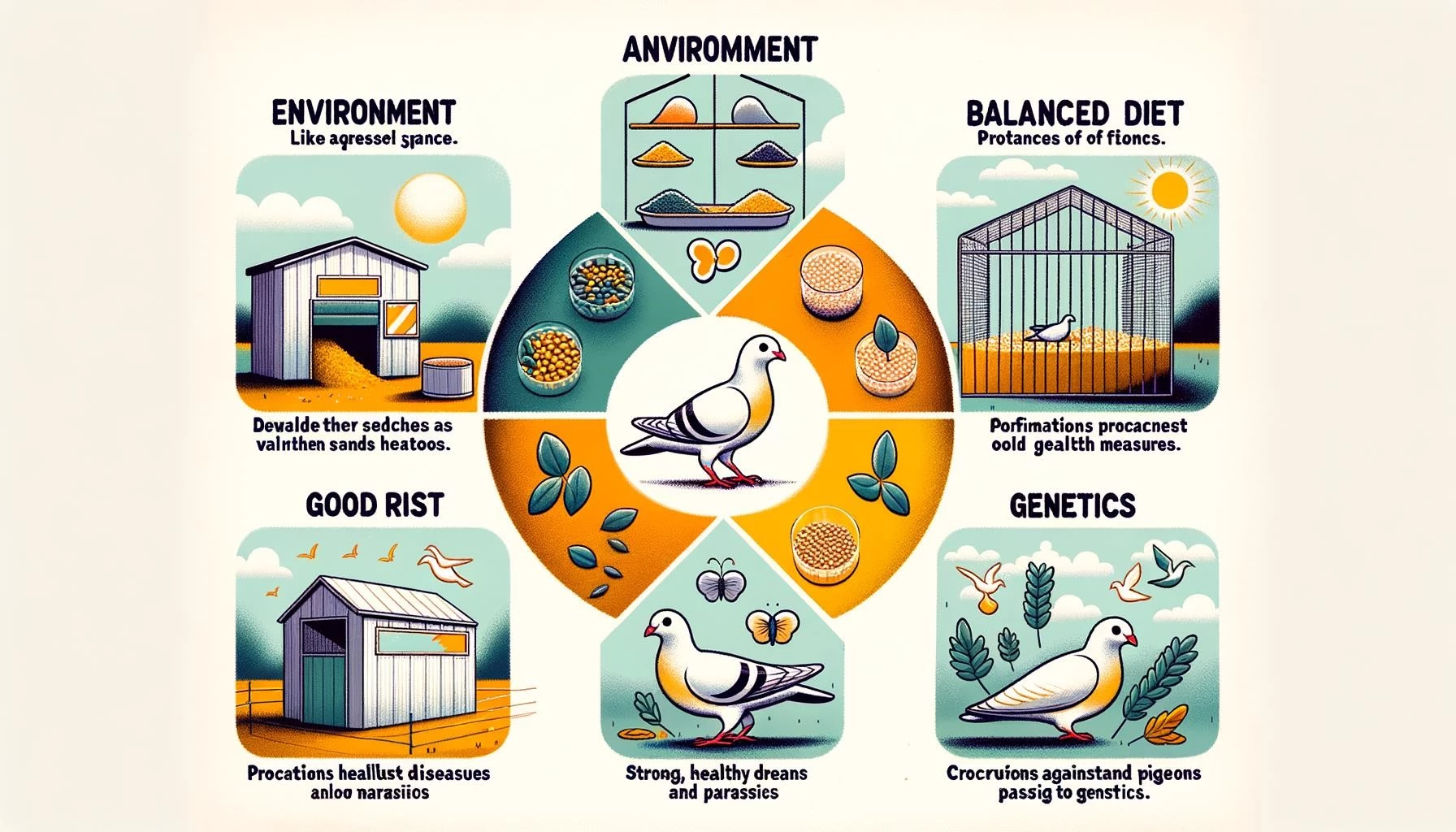
Factors Affecting Pigeon Breeding Success
Several factors contribute to the success of pigeon breeding. Here are some key considerations:
- Seasonal breeding patterns: Pigeons can breed year-round, but peak reproduction occurs in the spring and fall. Understanding the natural breeding patterns of pigeons can help breeders plan their breeding programs effectively.
- Breeding environment: Creating a comfortable breeding environment is essential for successful breeding. Pigeons require clean, well-ventilated lofts with adequate space for nesting and flying. Secure nesting boxes and appropriate nesting materials are also important.
- Proper nutrition: Providing adequate nutrition to breeder birds is crucial for their health and the success of breeding. Pigeons require a balanced diet that includes quality grains and supplements such as grit to support their reproductive processes.
- Care for breeder birds: Breeder birds require special care and attention throughout their reproductive journey. Proper nutrition, housing, timing, and diligent care contribute to the well-being of breeder birds and the success of breeding programs.
Genetic Diversity and Pigeon Breeding Success
Genetic diversity is important in pigeon breeding for maintaining the health and vitality of pigeon populations. Here are some key points regarding genetic diversity in pigeon breeding:
- Selective breeding: Selective breeding is a process in which pigeons with desirable traits are intentionally bred to produce offspring with those traits. This process can lead to a population with a higher frequency of these desired traits over generations.
- Maintaining diverse gene pools: It is important to avoid excessive inbreeding, as it can lead to negative effects on the health and vigor of pigeon populations. Pigeon breeders should select breeding pairs that maintain diverse gene pools to ensure long-term breeding success.
- Genetic compatibility: Pigeons have mate selection strategies that can influence breeding success and genetic diversity. Continued research is needed to understand the behaviors and factors involved in mate selection and their impact on breeding success.
- Color genetics: Breeders may also focus on specific color variations in pigeon breeding. Over generations, selective breeding for color traits can result in a population with a higher frequency of those desired colors.